on
How to Develop inside a Container using Visual Studio Code Remote Containers
I wrote this post originally for the 56K.Cloud Blog. You can find the original blog here.
 VS Code Remote-Containers
VS Code Remote-Containers
I joined 56K.Cloud in February, after having worked as a software developer for several years. I always try to make the lives easier for everybody involved in the development process. One VS Code feature that excels at this is the Visual Studio Code Remote - Containers extension. It is one of many extensions of the Visual Studio Remote Development feature.
This post is based on the work I did for the 56K.Cloud internal handbook. It uses Jekyll to generate a static website out of markdown files. This is a perfect example of how to make lives easier for everybody. Nobody should know how to install, configure, … Jekyll to make changes to the handbook. With the Remote Development feature, you add all the configurations and customizations to the version control system of your project. This means a small group implements it, and the whole team benefits.
One thing I need to mention is that as of now, this feature is still in preview. However, I never ran into any issues while using it, and I hope that it will get out of preview soon.
Prerequisites
You need to fulfil the following prerequisites, to use this feature:
- Install Docker and Docker Compose
- Install Visual Studio Code
- Install the Remote - Container extension
Enable it for an existing folder
The Remote - Container extension provides several ways to develop in a container. You can find more information in the documentation, with several Quick start sections. In this post, I will focus on how to enable this feature for an existing local folder.
As with all the other VS Code extensions, you also manage this with the Command Palette. You can either use the shortcut or the green button in the bottom left corner to open it. In the popup, search for Remote-Containers and select Open Folder in Container…
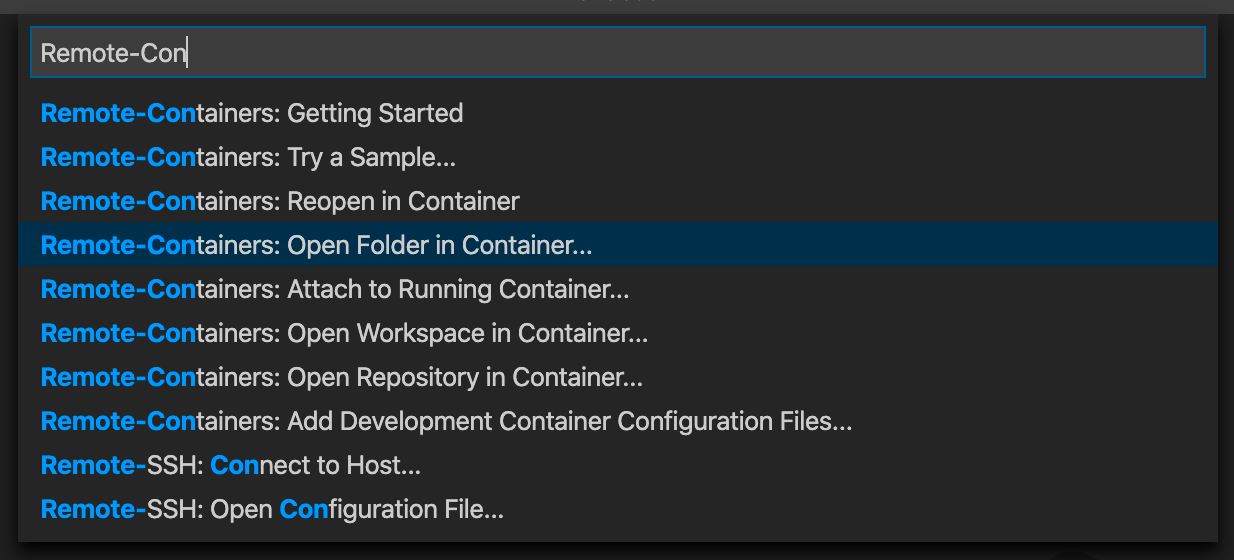 VS Code Command Palette
VS Code Command Palette
In the next popup, you have to select the folder which you want to open in the container. For this folder, you then need to Add the Development Container Configuration Files. VS Code shows you a list with predefined container configurations. In my case, I selected the Jekyll configuration. After that, VS Code starts building the container image and opens the folder in the container.
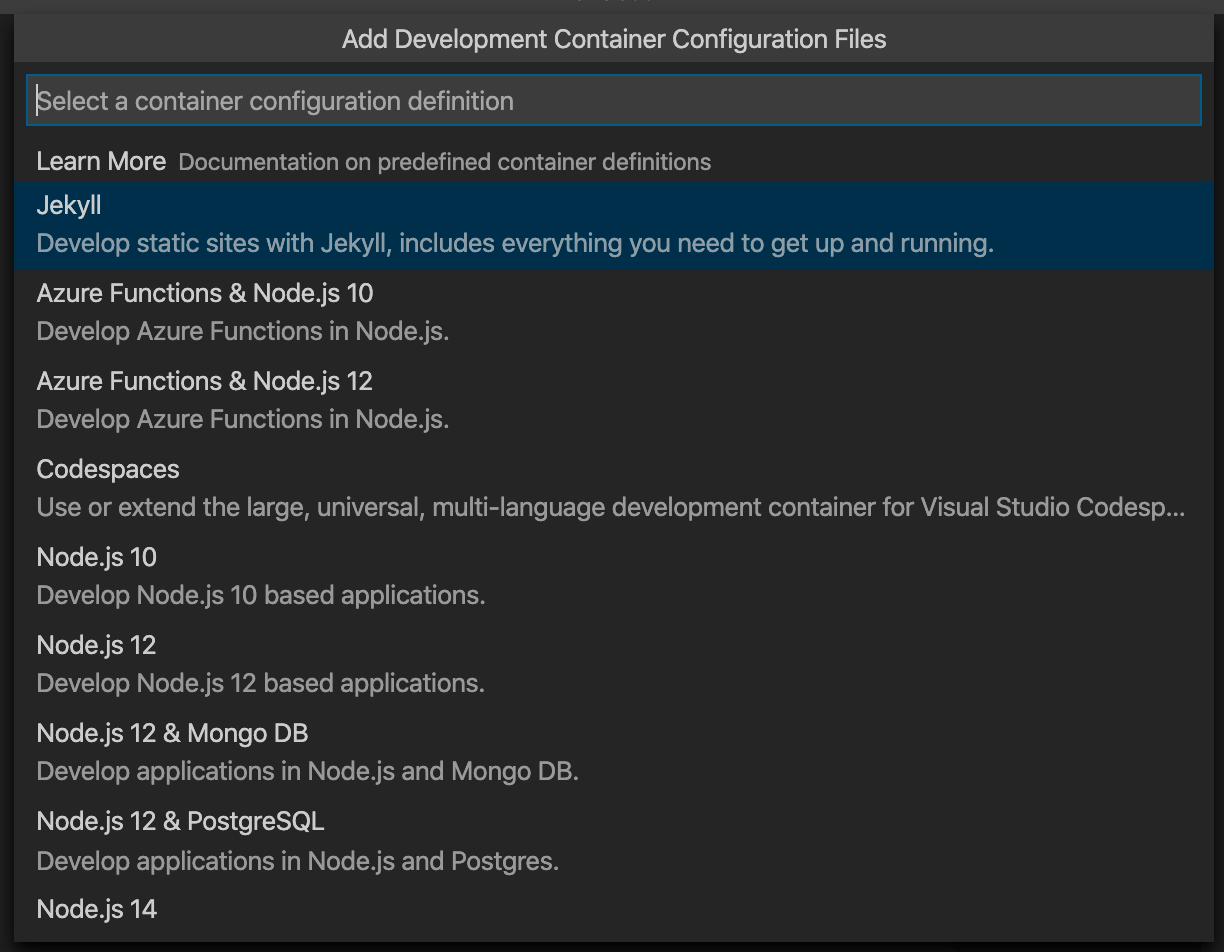 Add Development Container Configuration Files
Add Development Container Configuration Files
If you now have a look at the Explorer you can see, that there is a new folder
called .devcontainer. In my case, it added two files. The Dockerfile
contains all the instructions to build the container image. The
devcontainer.json contains all the needed runtime configurations. Some of the
predefined containers will add more files. For example, in the .vscode folder
to add useful Tasks. You can
have a look at the GitHub
Repo to find out more about
the existing configurations. There you can also find information about how to
use the provided template to write your own.
Customizations
The predefined container definitions provide a basic configuration, but you can
customize them. Making these adjustments is easy and I explain the two changes I
had to do below. The first was to install extra packages in the operating
system. To do so, I added the instructions to the Dockerfile. The second change
was to configure the port mappings. In the devcontainer.json, I uncommented the
forwardPorts attribute and added the needed ports. Be aware, for some changes
you just need to restart the container. Whereas for others, you need to rebuild
the container image.
Using and sharing
After you opened the folder in the container you can keep on working as you are used to. Even the terminal connects to the shell in the container. Whenever you open a new terminal, it will set the working directory to the folder you opened in the container. In my case, it allows me to type in the Jekyll commands to build and serve the site.
After I made all the configurations and customizations, I committed and pushed the new files to the git repository. This made them available to my colleagues, and they can benefit from my work.
Summary
Visual Studio Code supports multiple ways to do remote development. The Visual Studio Code Remote - Containers extension allows you to develop inside a container. The configuration and customizations are all part of your code. You can add them to the version control system and share them with everybody working on the project.
More Information
For more information about the topic you can head over to the following links:
- VS Code Remote Development
- Visual Studio Code Remote - Containers
- VS Code Remote Development Container Definitions - GitHub Repo
The Remote Container extension uses Docker as the container runtime. There is also a Docker extension, called: Docker for Visual Studio Code. Brian gave a very good introduction at DockerCon LIVE 2020. The recording of his talk Become a Docker Power User With Microsoft Visual Studio Code is available online.